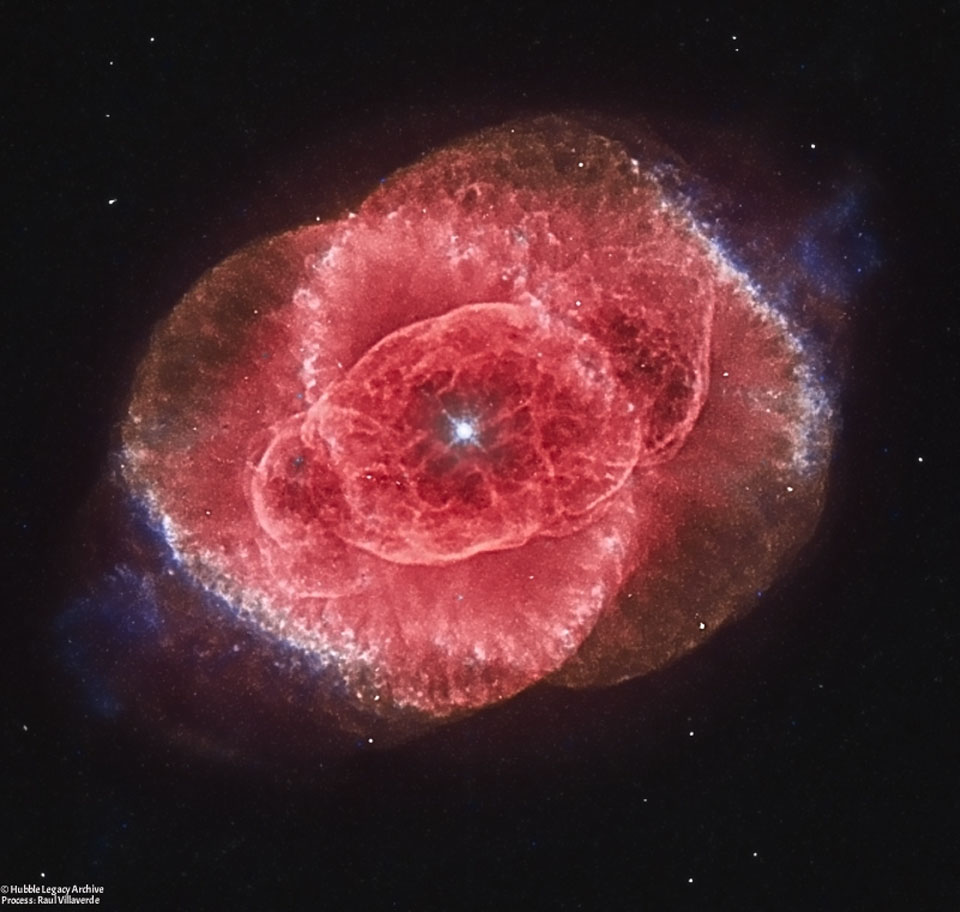
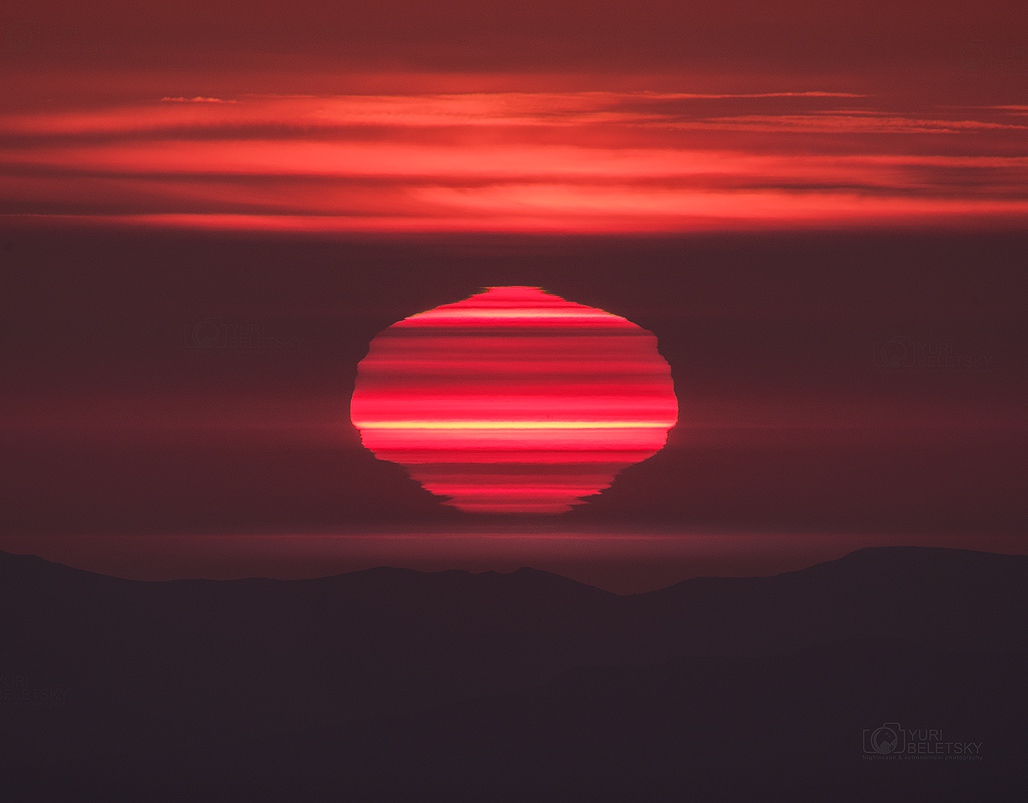
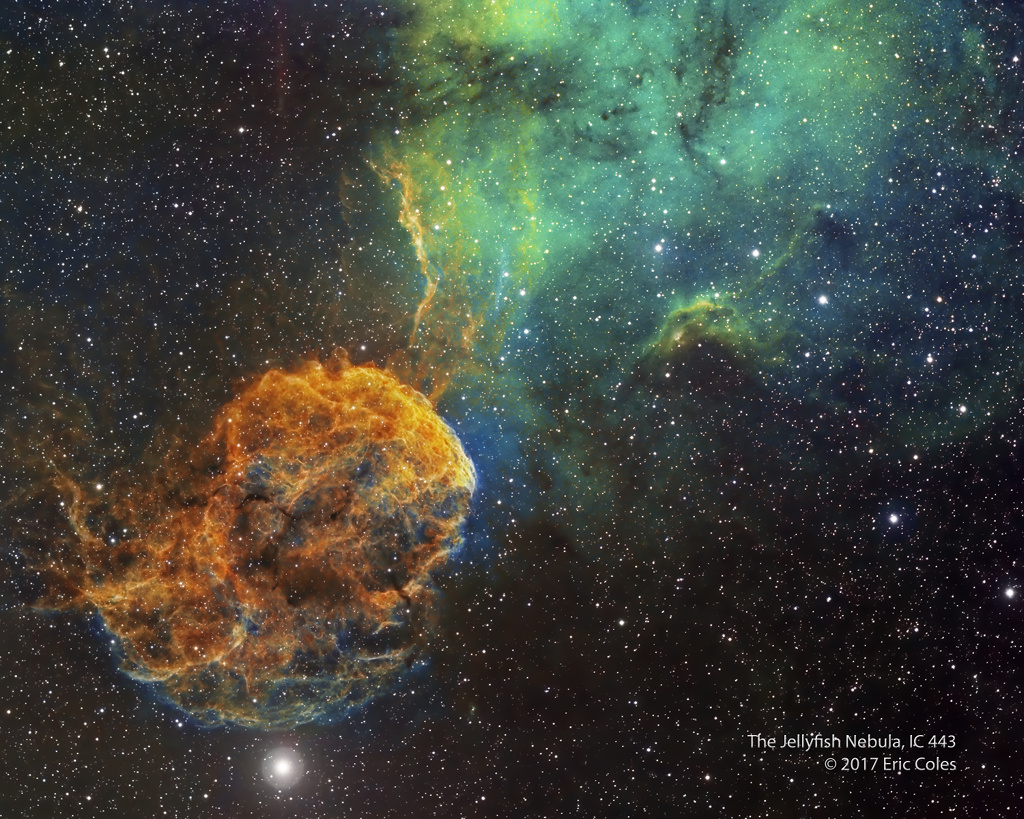
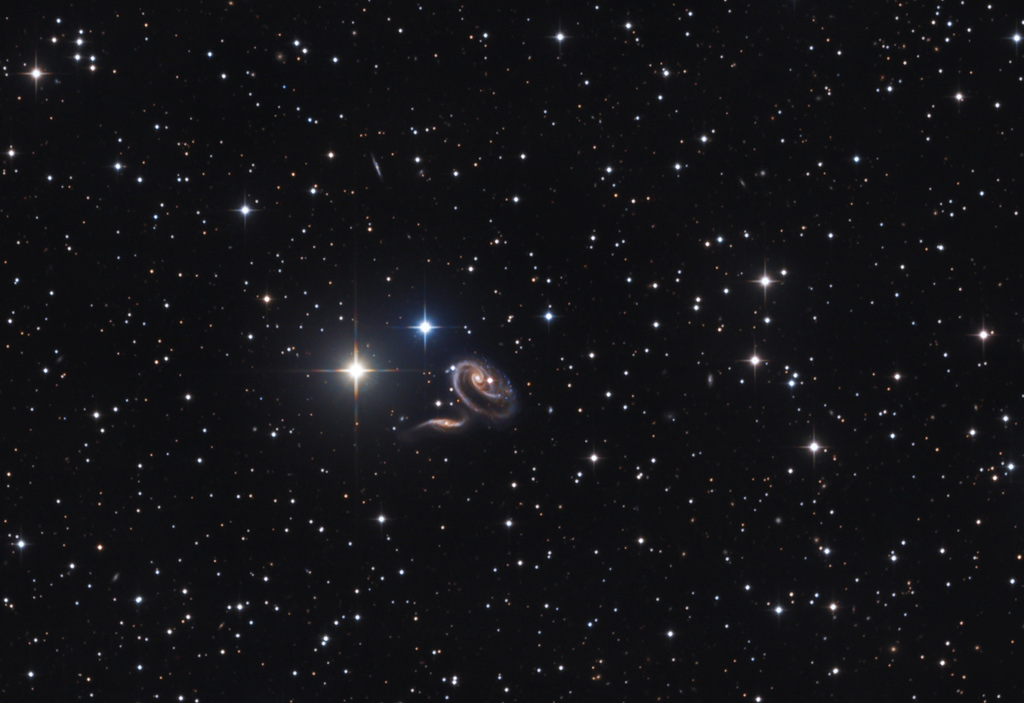
Martha Chaffee, widow of Roger Chaffee, Sheryl Chaffee, daughter, and Roger Purvenas, son of Sheryl Chaffee, left, along with acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot, right, place wreaths at the graves of Apollo 1 crewmembers Virgil "Gus" Grissom and Roger Chaffee as part of NASA's Day of Remembrance, Tuesday, Jan. 31, 2017. via NASA http://ift.tt/2jrXp4C