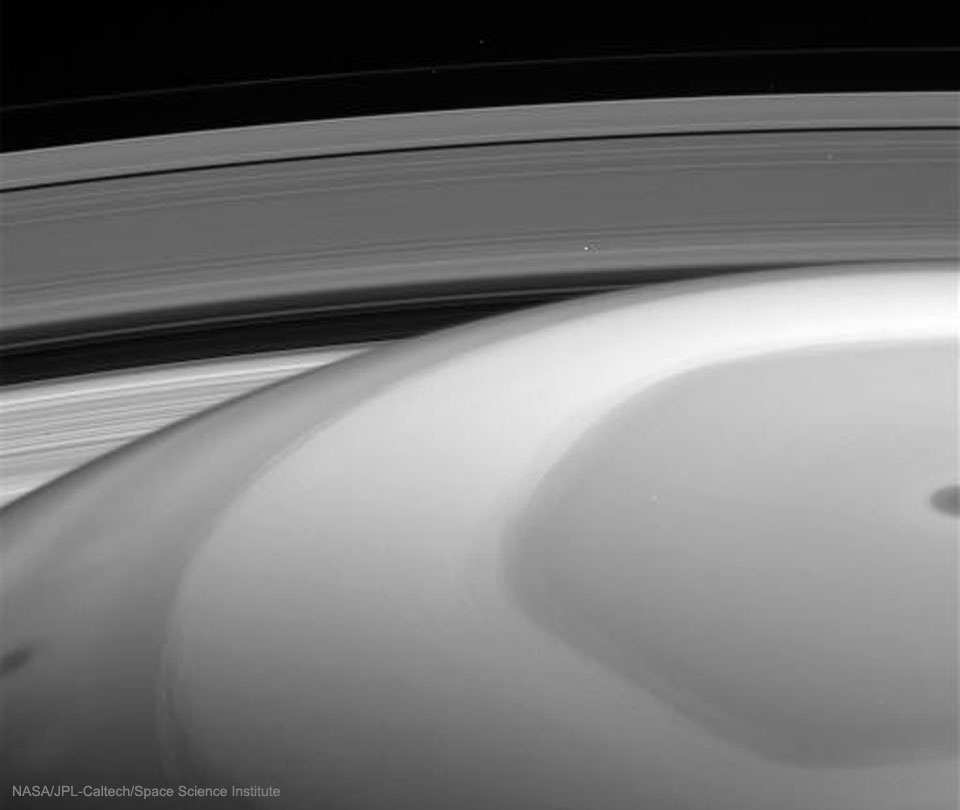
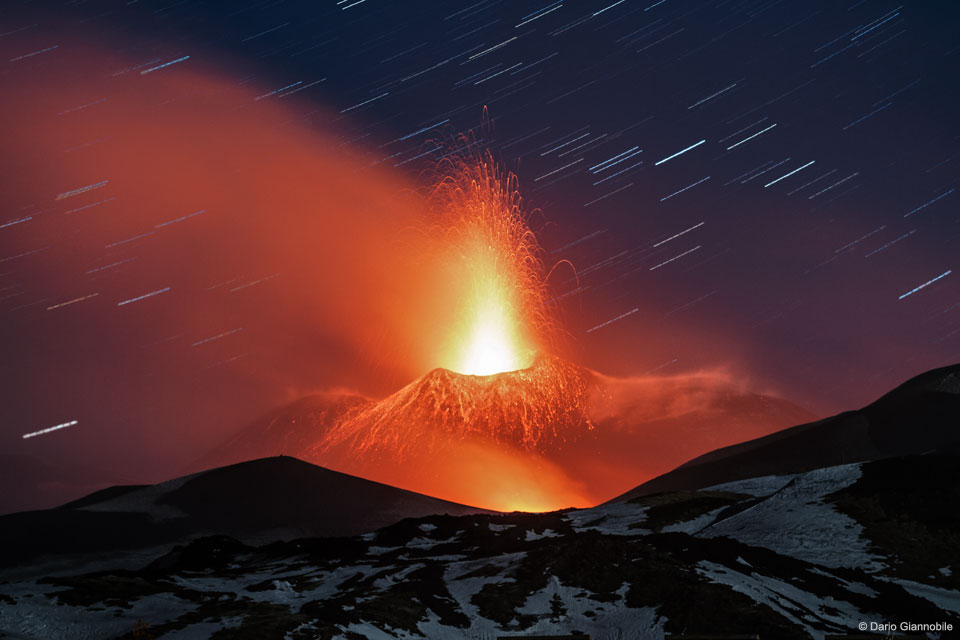
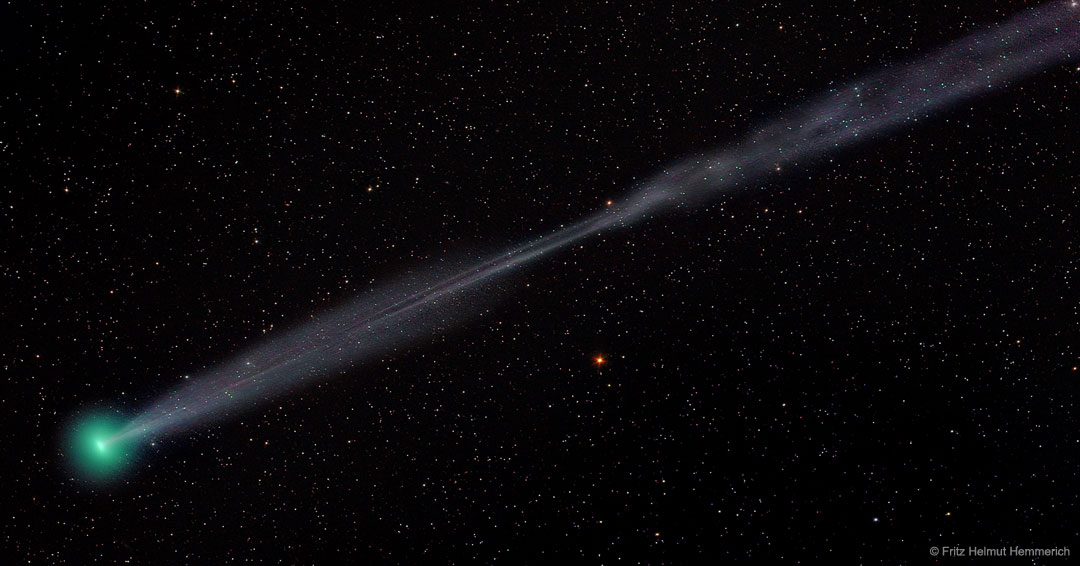
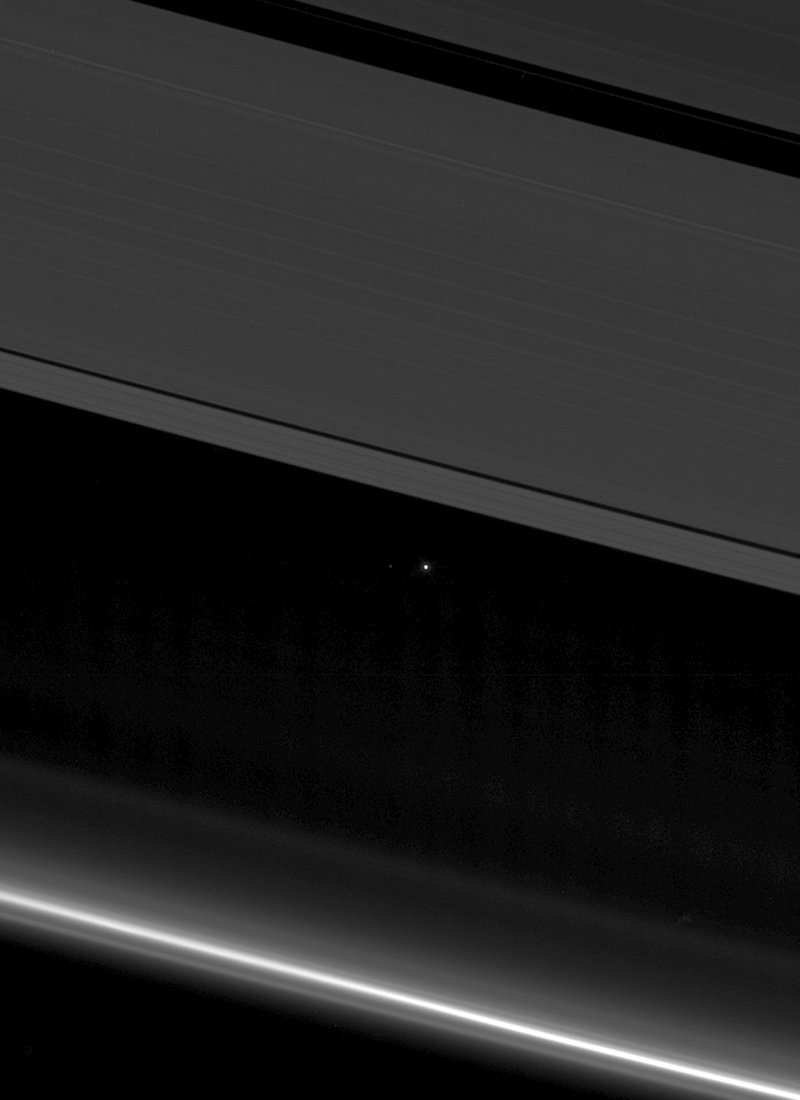
This is what Saturn looks like from inside the rings. Last week, for the first time, NASA directed the Cassini spacecraft to swoop between Saturn and its rings. During the dive, the robotic spacecraft took hundreds of images showing unprecedented detail for structures in Saturn's atmosphere. Looking back out, however, the spacecraft was also able to capture impressive vistas. In the featured image taken a few hours before closest approach, Saturn's unusual northern hexagon is seen surrounding the North Pole. Saturn's C ring is the closest visible, while the dark Cassini Division separates the inner B ring from the outer A. A close inspection will find the two small moons that shepherd the F-ring, the farthest ring discernable. This image is raw and will be officially verified, calibrated and released at a later date. Cassini remains on schedule to end its mission by plunging into Saturn's atmosphere on September 15. via NASA http://ift.tt/2oRAspc